In the world of steel fabrication, understanding the best techniques is essential for success. Renowned industry expert, John Smith, once stated, “Mastering steel fabrication techniques can set you apart from the competition.” This highlights the importance of knowledge and skill in this field.
Steel fabrication encompasses various processes that transform raw steel into precise components. Techniques can vary, from cutting and welding to assembly. Each step plays a crucial role in determining the final quality and strength of the product.
However, not all practices are perfected. Many professionals encounter challenges, such as equipment failures or miscalculations. These setbacks push the industry to innovate and improve. It’s vital to learn from mistakes and refine techniques continuously. A focus on quality and efficiency will drive progress in steel fabrication.

Steel fabrication plays a crucial role in construction and manufacturing. The techniques applied in this field define the quality and efficiency of projects. According to recent industry reports, the global steel fabrication market is projected to reach $309 billion by 2025. This growth reflects increasing demand across various sectors.
One prominent technique is welding, which joins metal pieces together. Various methods, such as MIG and TIG welding, provide flexibility in handling different thicknesses and materials. However, the quality of welds can vary. Inconsistent temperatures and material impurities often lead to weak joints that can compromise structural integrity.
Another key technique is machining, which involves cutting, drilling, and shaping steel. CNC machining allows for precision and repetition. Still, it can produce excessive waste. Some reports suggest that as much as 30% of raw materials can be lost during the machining process. This inefficiency calls for better practices in the industry to minimize waste and enhance sustainability.
Steel cutting and shearing are essential in fabrication. These methods shape steel for various applications. Common techniques include laser cutting, plasma cutting, and shearing. Each technique has its advantages and limitations.
Laser cutting offers precision and clean edges. It uses a focused beam to cut through steel. However, it may be slower for thicker materials. Plasma cutting, on the other hand, uses ionized gas to slice through metal. It's fast and suitable for various thicknesses but can leave rough edges. Shearing is a mechanical method that creates straight cuts. While it's efficient for sheets, it can be less effective for intricate designs.
Choosing the right method depends on the project needs. Factors include material type, thickness, and desired finish. It's essential to evaluate these before proceeding. Understanding these techniques helps in making informed decisions. Mistakes can lead to wasted materials and time. With practice, one can master the basics and improve results.
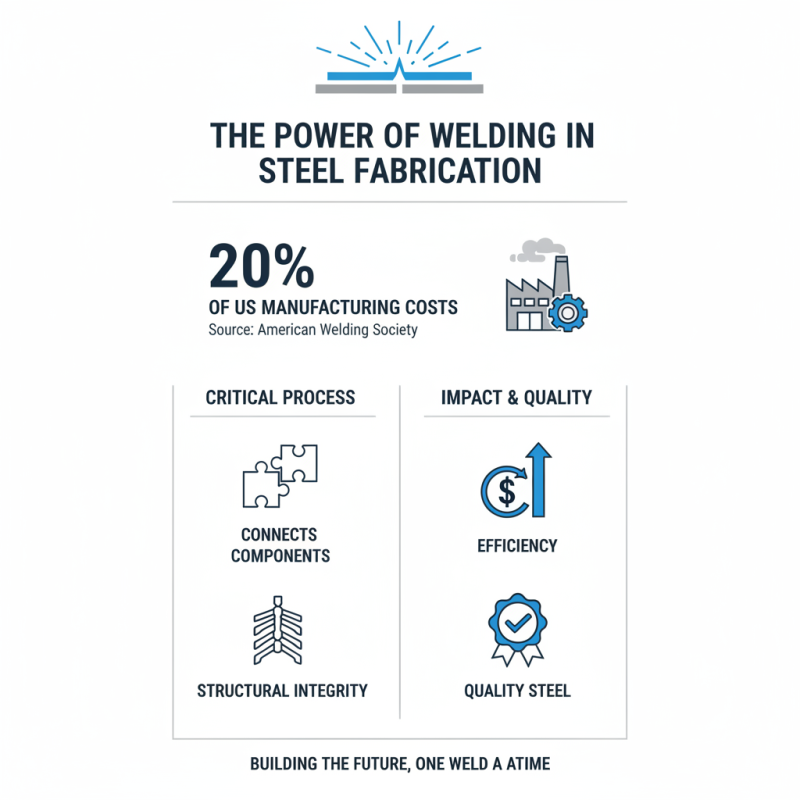
Welding is a critical process in steel fabrication. It connects components and provides structural integrity. According to the American Welding Society, welding accounts for approximately 20% of manufacturing costs in the U.S. This suggests its significance in the overall efficiency and quality of steel structures.
There are various welding techniques used in the industry. MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding is prevalent due to its speed and versatility. It’s ideal for thin materials but may produce less durability. On the other hand, TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding offers more precision and is perfect for complex joints. However, TIG can be time-consuming and requires a skilled operator.
Interestingly, a study by the International Institute of Welding shows that more errors occur in MIG than in TIG. This raises questions about training and quality control practices. While each method has pros and cons, choosing the right one is crucial. The demand for skilled welders remains high, but many new entrants lack adequate experience. The industry needs to prioritize training to mitigate these issues.
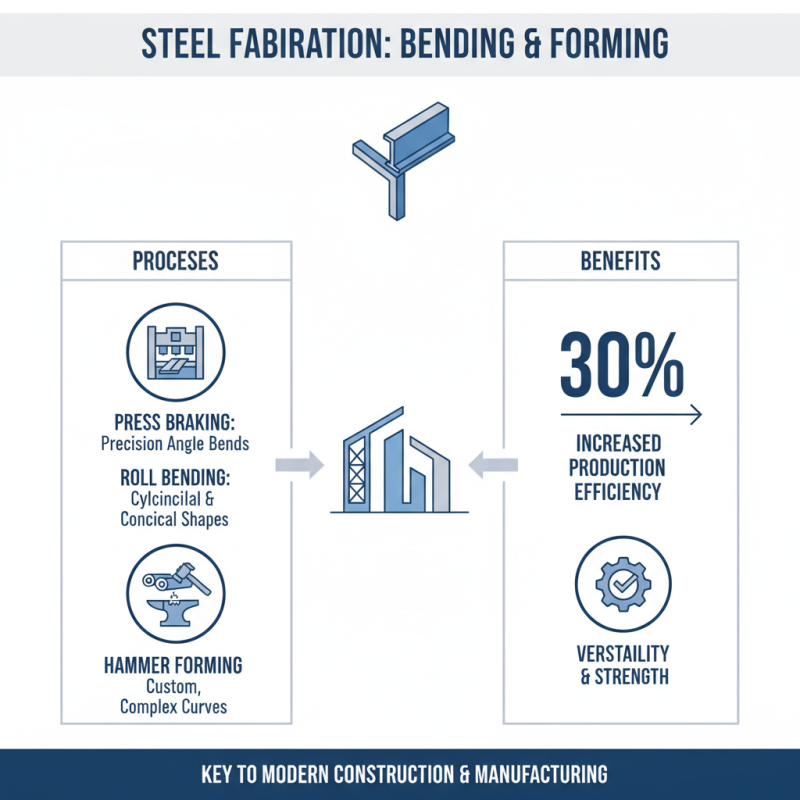
Bending and forming processes are vital in steel fabrication. These techniques shape steel into various forms for construction and manufacturing. The processes can include techniques like press braking, roll bending, and hammer forming. Each has its unique applications and advantages. According to industry data, bending can increase production efficiency by 30% when implemented correctly.
Press braking is one of the most common methods. It involves a machine that bends steel sheets into precise angles. This method is ideal for creating parts like brackets and frames. However, it's essential to consider the machine's capacity. Too much force can cause defects in the steel.
Tips: Always test your setup before full production. Check alignment and force settings.
Roll bending is another interesting technique. It allows for the creation of cylindrical parts, used in structures like pipes. Getting the radius correct is crucial. An incorrect bend can lead to material wastage.
Tips: Use precise measurements to avoid costly errors. Regular maintenance of equipment is also essential.
Improper techniques can lead to cracks or weak points in the steel. Knowledge of each method plays a vital role in successful fabrication. Educate your team continually to ensure high-quality results.
Quality control is crucial in steel fabrication. It ensures that every piece meets industry standards. Regular inspections can prevent defects. These inspections can be as simple as checking dimensions. However, many overlook this step. Small errors can lead to major issues.
Safety measures are equally important. Steel fabrication involves heavy machinery. Workers must wear appropriate gear. Protective equipment significantly reduces injury risks. It's essential to conduct safety training. Yet, not all companies prioritize this. Inadequate training can result in accidents.
Effective communication is vital on the shop floor. Misunderstandings can lead to unsafe conditions. Team members should voice concerns openly. Encouraging dialogue fosters a safer work environment. Despite knowing this, some workers hesitate to speak up. A culture of safety must be actively nurtured.